TreeMap chart
(quoted from Treemap chart definition in Wikipedia)
In information visualization and computing, treemapping is a method for displaying hierarchical data using nested figures, usually rectangles.
Treemaps display hierarchical (tree-structured) data as a set of nested rectangles. Each branch of the tree is given a rectangle, which is then tiled with smaller rectangles representing sub-branches. A leaf node's rectangle has an area proportional to a specified dimension of the data. Often the leaf nodes are colored to show a separate dimension of the data.
When the color and size dimensions are correlated in some way with the tree structure, one can often easily see patterns that would be difficult to spot in other ways, such as whether a certain color is particularly relevant. A second advantage of treemaps is that, by construction, they make efficient use of space. As a result, they can legibly display thousands of items on the screen simultaneously.
Charba provides out of the box the feature to enable treemap chart, leveraging on Chart.js Treemap.
The Chart.js Treemap is native javascript implementation and Charba provides the wrapper in order to be able to use it.
Programmatically, you could use a bar chart as following:
// creates the chart
TreeMapChart chart = new TreeMapChart();
// adds to DOM
component.add(chart);
...
// example for Elemental2
// gets the chart instance as DOM element
Element element = chart.getChartElement().as();
// adds to DOM
DomGlobal.document.body.appendChild(element);
By UIBinder (ONLY for GWT), you could use a bar chart as following:
<ui:UiBinder xmlns:ui="urn:ui:com.google.gwt.uibinder"
xmlns:g="urn:import:com.google.gwt.user.client.ui"
xmlns:c="urn:import:org.pepstock.charba.client.gwt.widgets">
<g:HTMLPanel width="100%">
....
<c:TreeMapChartWidget ui:field="chart"/>
...
</g:HTMLPanel>
</ui:UiBinder>
Dataset
The treemap chart allows to define the data and a number of properties, used to display the data, by a treemap dataset.
Every chart has got a method to create a typed dataset accordingly with the chart type. The dataset can be also created instantiating the constructor.
// creates the chart
TreeMapChart chart = new TreeMapChart();
// creates the dataset
TreeMapDataset dataset = chart.newDataset();
// sets the option
dataset.setBackgroundColor(HtmlColor.RED);
...
// creates the dataset
TreeMapDataset datasetNew = new TreeMapDataset();
// sets the option
datasetNew.setBackgroundColor(HtmlColor.RED);
...
// sets the dataset to the chart
chart.getData().setDatasets(dataset);
The following are the attributes that you can set:
| Name | Type | Default | Scriptable | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| backgroundColor | String[] - IsColor[] - Pattern[] - Gradient[] | Defaults.get().getGlobal().getBackgroundColorAsString() | Yes | The fill color/pattern of the treemap element. |
| borderColor | String[] - IsColor[] - Gradient[] | Defaults.get().getGlobal().getBorderColorAsString() | Yes | The color of the treemap element border. |
| borderWidth | int[] | 0 | - | The stroke width of the treemap element in pixels. |
| color | String[] - IsColor[] | HtmlColor.TRANSPARENT | Yes | Color of label. See default colors. |
| dividerCapStyle | CapStyle | CapStyle.BUTT | - | Cap style of the divider inside a treemap element. See MDN. |
| dividerColor | String[] - IsColor[] | HtmlColor.BLACK - | - | The color of the divider inside a treemap element. |
| dividerWidth | int[] | 0 | - | The stroke width of the divider inside a treemap element in pixels. |
| dividerDash | Dash[] | [] | - | Length and spacing of dashes of the divider inside a treemap element. See MDN. |
| dividerDashOffset | double | 0 | - | Offset for line dashes of the divider inside a treemap element. See MDN. |
| font | IsFont | Defaults.get().getGlobal().getFont() | - | Font of text of label. See Font. |
| groupDividers | boolean | false | - | If true, the dividers will be applied to the grouped treemap elements, only if grouping. |
| groupLabels | boolean | true | - | If true, the labels will be applied to the grouped treemap elements, only if grouping. |
| groups | String[] - Key[] | [] | - | Set the properties names of the tree object to group by the data. |
| hoverBackgroundColor | String[] - IsColor[] - Pattern[] - Gradient[] | Defaults.get().getGlobal().getBackgroundColorAsString() | Yes | The fill color/pattern of the treemap elements when hovered. |
| hoverBorderColor | String[] - IsColor[] - Gradient[] | Defaults.get().getGlobal().getBorderColorAsString() | Yes | The stroke color of the treemap elements when hovered. |
| hoverBorderWidth | int[] | 0 | - | The stroke width of the treemap elements when hovered. |
| hoverColor | String[] - IsColor[] | HtmlColor.TRANSPARENT` | Yes | Color of label, when hovered. See default colors. |
| hoverFont | IsFont | Defaults.get().getGlobal().getFont() | - | Font of text of label, when hovered. See Font. |
| key | Key | null | - | Set the property name of the tree object to use to get the value of the data. |
| rtl | boolean | false | - | Set true for rendering the treemap elements from right to left. |
| spacing | double | 0.5D | - | Fixed distance between all treemap elements. |
Scriptable
Scriptable options at dataset level accept a callback which is called for each of the underlying data values. See more details in Configuring charts section.
// creates chart
TreeMapChart chart = new TreeMapChart();
// creates dataset
TreeMapDataset dataset = chart.newDataset();
// sets the option by a callback
dataset.setBackgroundColor(new ColorCallback<DatasetContext>(){
@Override
public IsColor invoke(DatasetContext context){
// logic
return color;
}
});
The following options can be set by a callback:
| Name | Callback | Returned types |
|---|---|---|
| backgroundColor | ColorCallback<DatasetContext> | String - IsColor - Pattern - Gradient |
| borderColor | ColorCallback<DatasetContext> | String - IsColor - Gradient |
| color | ColorCallback<DatasetContext> | String - IsColor |
| hoverBackgroundColor | ColorCallback<DatasetContext> | String - IsColor - Pattern - Gradient |
| hoverBorderColor | ColorCallback<DatasetContext> | String - IsColor - Gradient |
| hoverColor | ColorCallback<DatasetContext> | String - IsColor |
Data structure
The data of a dataset for a treemap chart can be passed in two formats. The data are automatically built, based on the tree data, provided by the users.
The setData and setDataPoints methods are available, inherited by the bar dataset, but you can NOT use them otherwise an exception will throw.
Use setTree or setTreeObjects instead.
The getDataPoints methods is available and can provide a list of TreeMapDataPoint.
Data as doubles
A treemap dataset can contain the data as an array or list of doubles,
// creates chart
TreeMapChart chart = new TreeMapChart();
// creates dataset
TreeMapDataset dataset = chart.newDataset();
// sets data as an array of doubles
dataset.setTree(1,2,3,4,6);
// sets data as a list of double
List<Double> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
dataset.setTree(list);
Data as objects
Tree data should be provided by a list of objects. Data is then automatically build. When the data are provided by objects, the key dataset property defines the key name in data objects to use for value, and the groups dataset property, as list of keys, can be provided to display multiple levels of hierarchy. Data is summarized to groups internally.
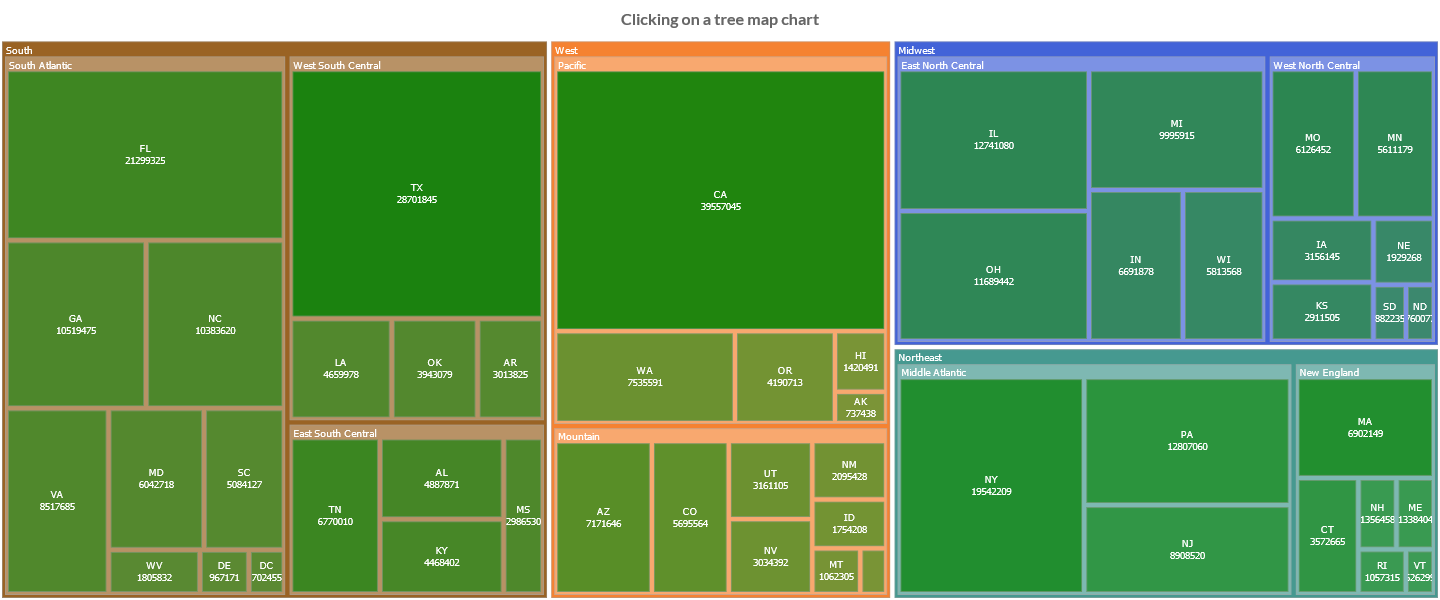
// list of TreeMapObject properties
private enum Property implements Key
{
STATE("state"),
CODE("code"),
REGION("region"),
DIVISION("division"),
INCOME("income"),
POPULATION("population"),
AREA("area");
private final String value;
private Property(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String value() {
return value;
}
}
// tree objects type
private static class TreeMapObject extends NativeObjectContainer {
private TreeMapObject(NativeObject nativeObject) {
super(nativeObject);
}
}
// creates the tree objects
List<TreeMapObject> objects = new LinkedList<>();
// creates or loads objects from external source
...
// creates chart
TreeMapChart chart = new TreeMapChart();
// creates dataset
TreeMapDataset dataset = chart.newDataset();
// sets data as an array of doubles
dataset.setTreeObjects(objects);
// sets the value by the key of the object
dataset.setKey(Property.POPULATION);
// sets the keys of the object to group by
dataset.setGroups(Property.REGION, Property.DIVISION, Property.CODE);
Options
The treemap chart defines specific options implementation to be configured.
// creates the chart
TreeMapChart chart = new TreeMapChart();
// gets the chart options
TreeMapOptions options = chart.getOptions();
// sets option
options.setResponsive(true);
The treemap chart disables the DATALABELS, LABELS, ZOOM, ANNOTATION, HTML legend and dataset items selector plugins and the options can NOT be set globally but only at chart level.